Diffusion Properties Of Ceramic Membranes

During dd process in some cases the waste solution containing some solid wastes can lead to the block and pollution of the membrane the decrease of the treatment efficiency and membrane service life.
Diffusion properties of ceramic membranes. Hence in the last. Tang in membrane based salinity gradient processes for water treatment and power generation 2018. Lastly membrane curvature can play a role in the obstruction of diffusion figure10. Commercial ceramic membranes are made by sintering or sol gel processes them.
Ceramic membranes could be made from such materials forming the major class of inorganic membranes with aluminum oxide α al 2 o 3 or alumina and zirconium oxide or zirconia as the most important representatives. Despite outstanding properties the efforts in developing ceramic membranes as a replacement for polymeric membranes in md desalination are meeting challenges and obstacles. Zhe yang chuyang y. The bent region of the membrane has distinct properties as the head groups of the lipids constituting the concave monolayer are unusually close whereas the head groups on the convex monolayer are uncharacteristically far apart.
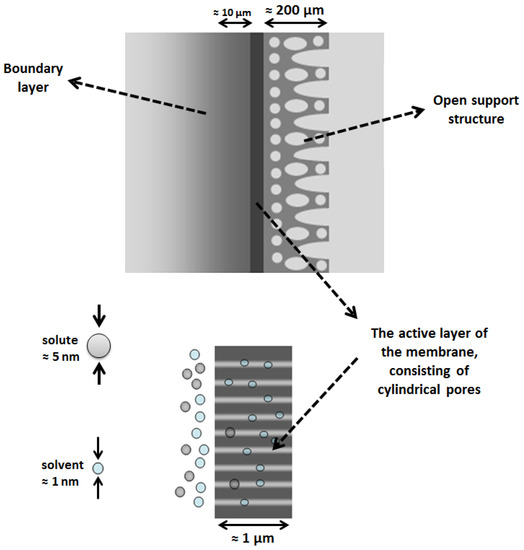
Permeability coefficients calculated from diffusion experiments are found to be approximately three times higher in hydrophilic membrane than. Most ceramic membranes are made of alumina titania silica zirconia or mixture of these materials 93 the basic structure of ceramic membranes consists of a macroporous support layer and meso or microporous active layer. The rate of diffusion depends apart from the lipid water partition coefficient of the drug p and the concentration gradient c out c in on membrane properties such as the membrane area a and thickness h and the diffusion coefficient d of the drug in the membrane according to fick s law. Diffusion dialysis integrated with ceramic membrane microfiltration.
The diffusion measurements are performed using a diffusion cell during 10 h at 37 degrees c. Adsorption isotherms and diffusion coefficients for n c4 and i c4 in the transport pathways through tubular zsm 5 zeolite membranes were determined over a range of temperatures by a transient permeation method. Many attempts have been made by researchers to produce ceramic membranes with modified. The membranes are prepared by solvent casting method and characterized by ftir spectra and sem analysis.
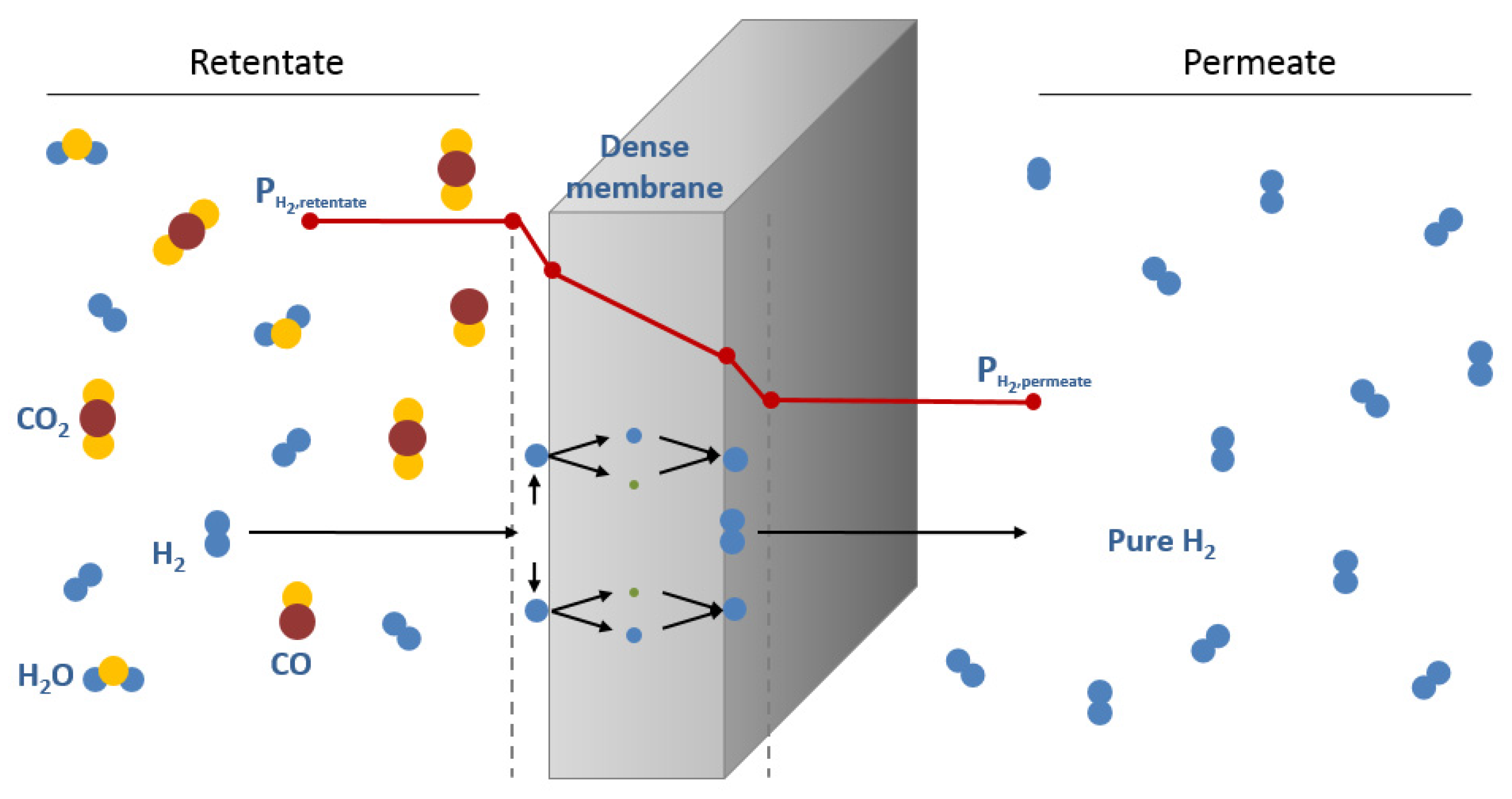
The permeate response to step changes in the feed were measured and the transport was modeled as maxwell stefan diffusion with single site langmuir adsorption in the zeolite. In the case of membranes diffusion along with pore flow is the main transport mechanism. Accordingly the waste solution should be purified before dd process.